Understanding Alopecia Areata
Alopecia areata is not just a simple cosmetic concern; it goes beyond the superficial patches of hair loss. While often recognized by its characteristic bald spots, the emotional and psychological effects of this condition run deep. But what exactly is alopecia areata, and why does it matter?
Read the rest of the article to find out…
Table of Contents
1.1 An In-depth Overview of Alopecia Areata
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system attacks the hair follicles, leading to hair loss. It’s not limited to the scalp; it can affect any part of the body with hair, including the eyebrows, eyelashes, and beard. Unlike other forms of hair loss, where thinning occurs gradually, alopecia often results in rapid and unpredictable hair loss in small, round patches.
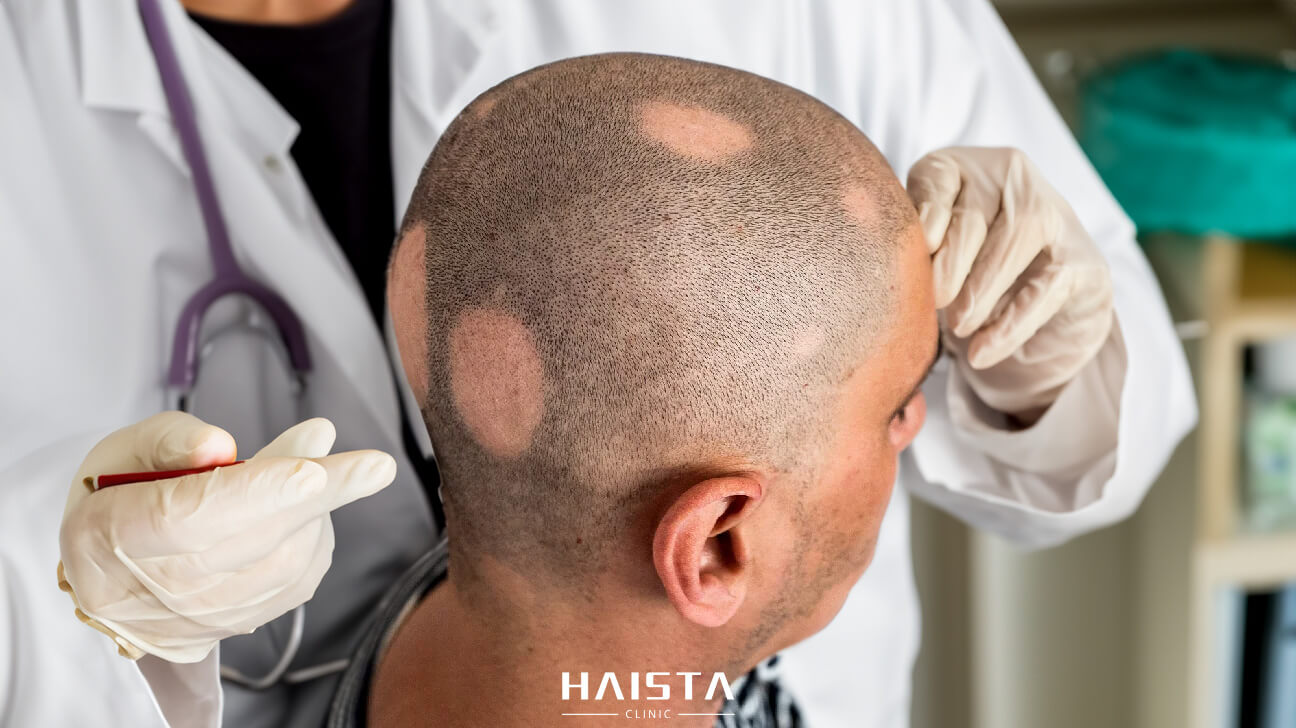
The exact cause of alopecia remains a mystery, but several factors play a role. Genetic predisposition, coupled with external triggers like stress or a viral infection, can set the stage for an autoimmune response against the hair follicles.
Interestingly, it’s not just the hair that’s affected. The skin underneath the bald patches remains healthy and devoid of scars. This is a crucial aspect because it means the hair follicles are still alive and hair can regrow, given the right circumstances. In fact, many individuals experience spontaneous regrowth, though the hair may initially come back white or finer than before.
For those looking into hair restoration solutions, there are several options available, including hair transplant surgery. However, it’s vital to consult with a specialist to determine the best approach, especially given the unpredictable nature of alopecia areata.
1.2 The Prevalence and Rapid Onset of Alopecia Areata
Alopecia areata affects both genders and can occur at any age, although it’s most common in people younger than 30. Worldwide, it’s estimated that approximately 2% of the population will experience alopecia at some point in their lives. This translates to millions of people grappling with the sudden and unexpected onset of hair loss.
The speed at which alopecia areata manifests can be startling. One could have a full head of hair one month and then discover multiple bald patches the next. The unpredictable nature of the condition, combined with its visible effects, can be emotionally challenging. Feelings of embarrassment, frustration, and decreased self-esteem are common among individuals with alopecia areata.
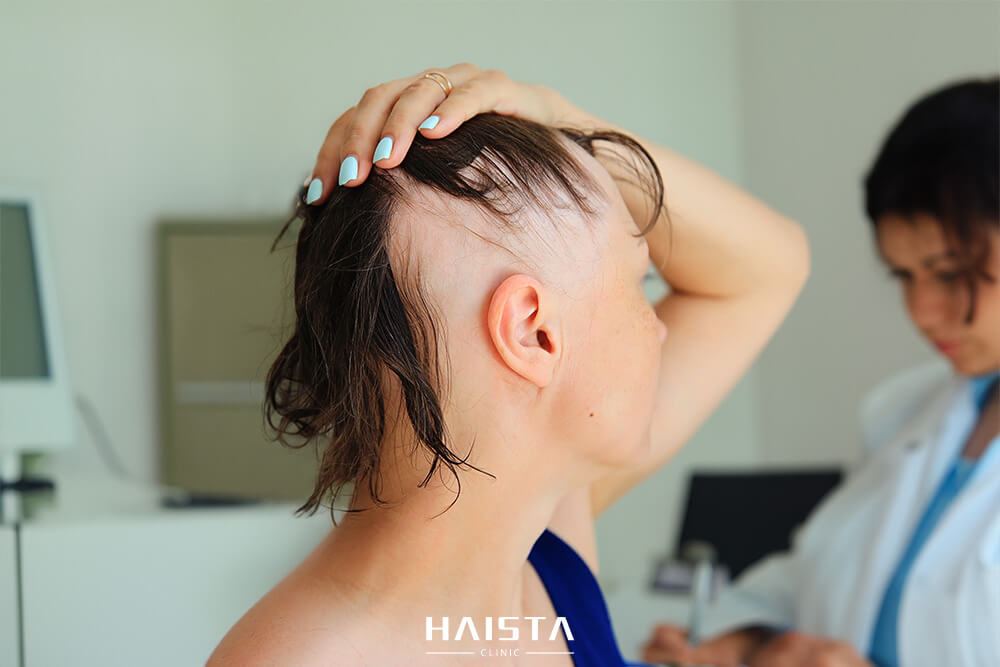

For women, who often face societal pressure regarding appearance, hair loss can be particularly distressing. While alopecia affects both genders, the emotional ramifications can differ. It’s essential to recognize and address these feelings. For women seeking guidance on hair-related issues, resources like this comprehensive guide on women’s hair loss and thinning hair causes and solutions can be invaluable.
In conclusion, alopecia is more than just patchy hair loss. It’s a condition that affects the individual both physically and emotionally. Understanding its nature and prevalence is the first step toward managing and potentially treating it.
2. Unraveling the Mysteries: Causes and Risk Factors of Alopecia Areata
Delving deeper into the world of alopecia, it’s essential to understand the myriad causes and risk factors that contribute to its onset. While the exact reasons remain elusive, significant strides have been made in shedding light on the various elements at play.
2.1 The Autoimmune Link to Alopecia Areata
Central to the development of alopecia areata is the role of the immune system. In most cases, our immune system acts as a defense mechanism, warding off infections and diseases. However, in the case of alopecia areata, there’s a misdirection of this protective function. The immune system mistakenly identifies hair follicles as foreign invaders and launches an attack. This autoimmune response leads to inflammation around the hair follicle, inhibiting hair growth and resulting in characteristic bald patches.
2.2 Genetic Connections: Does It Run in the Family?
There’s compelling evidence to suggest that genetics play a role in the susceptibility to alopecia. Studies have shown that individuals with a family history of the condition are at a higher risk of developing it themselves. Specific genes have been identified that increase the likelihood, but the presence of these genes alone doesn’t guarantee onset. Instead, it indicates a heightened vulnerability, especially when combined with other triggers.
2.3 Environmental and Lifestyle Triggers
While genetics can predispose an individual to alopecia areata, environmental and lifestyle factors often act as the spark that ignites the condition. Some of the known triggers include:
- Viral infections: Certain viruses can stimulate the immune system in a way that leads it to target hair follicles.
- Physical trauma: Injuries or surgeries can sometimes lead to the development of alopecia in previously unaffected individuals.
- Hormonal changes: Events such as pregnancy, menopause, or thyroid imbalances can act as triggers.
2.4 Association with Other Autoimmune Conditions
Alopecia areata doesn’t exist in isolation. It’s often seen in tandem with other autoimmune conditions. For instance, individuals with alopecia areata have a higher likelihood of developing conditions like thyroiditis, vitiligo, or rheumatoid arthritis. Understanding this association can help in early detection and holistic management of the individual’s health.
2.5 The Role of Emotional and Psychological Stress
There’s a growing body of evidence that underscores the role of emotional and psychological stress in the onset and exacerbation of alopecia. Stressful events, whether they be personal, professional, or health-related, can act as triggers. The body’s response to stress can lead to inflammation, which, in susceptible individuals, targets the hair follicles.
Moreover, the onset of alopecia can, in turn, cause significant stress, creating a vicious cycle. Addressing the emotional aspects and seeking support, whether through counseling or support groups, is crucial for overall well-being.
In wrapping up this section, it’s evident that alopecia is a multifaceted condition with a multitude of causes and risk factors. A holistic approach, taking into account genetics, lifestyle, other health conditions, and emotional well-being, is key to understanding and managing it.
3. Identifying Alopecia Areata: Types and Symptomatic Patterns
Alopecia areata, while primarily recognized for its characteristic bald patches, actually manifests in various forms and patterns. It’s imperative to understand and distinguish between these types, as each has its own unique symptomatic profile, prognosis, and management considerations.
3.1 Spotlight on Patchy Alopecia Areata
Patchy Alopecia Areata is the most common form of this condition. It’s characterized by one or multiple circular bald patches that can appear anywhere on the scalp. These patches are typically smooth and devoid of any scarring, indicating that the hair follicles remain alive underneath. Over time, these patches may either resolve spontaneously, expand, or merge with other patches. Notably, in many instances, the hair regrows within these patches, although it may initially be of a lighter color or texture.
3.2 Grasping Alopecia Totalis and Universalis
Alopecia Totalis and Alopecia Universalis are the more severe and extensive manifestations of alopecia areata.
- Alopecia Totalis: This form results in total hair loss on the scalp. It goes beyond the scattered patches seen in the patchy variant and affects the entire scalp, leading to complete baldness. This type can be particularly distressing given its visibility and the cultural importance often attached to scalp hair.
- Alopecia Universalis: This is the most extensive form, leading to hair loss across the entire body, not just the scalp. This includes eyebrows, eyelashes, facial hair, pubic hair, and even the fine vellus hair that covers most of the skin. Individuals with alopecia universalis need to be particularly mindful of other potential complications, such as increased vulnerability to sunburn or eye irritations due to the loss of eyelashes.
3.3 Distinguishing Diffuse Alopecia Areata and Ophiasis
While the above forms are more straightforward, there are other patterns that might be less recognized but are equally important to identify:
- Diffuse Alopecia Areata: Instead of distinct patches, this form presents as a sudden and widespread thinning of hair across the scalp. It can sometimes be mistaken for other forms of hair loss, like telogen effluvium or androgenetic alopecia. Proper diagnosis is essential, as the management and prognosis can differ.
- Ophiasis Alopecia Areata: This form has a unique pattern, with hair loss occurring in a band-like distribution along the sides and lower back of the scalp. ‘Ophiasis’ is derived from the Greek word for ‘snake’, referencing the snake-like pattern of hair loss. This type can be more resistant to treatment compared to patchy alopecia areata.
In understanding these varied manifestations of alopecia areata, one can appreciate the complexity of the condition. Proper identification is paramount, as it guides both the therapeutic approach and the patient’s expectations. Whether it’s the more common patchy type or the extensive alopecia universalis, each form requires a tailored strategy, ideally formulated in consultation with a specialist, like those at renowned centers such as Haista Clinic.
4. Hope Amidst Hair Loss: Can Hair Regrow with Alopecia Areata?
Alopecia areata, while presenting significant challenges, is not a condition devoid of hope. One of the silver linings is the potential for hair regrowth. However, understanding the nuances of this regrowth, the factors that influence it, and the potential for recurrence is crucial for setting realistic expectations and strategies for management.
4.1 Factors Influencing Hair Regrowth
While many individuals with alopecia experience hair regrowth, the extent and speed can vary widely. Several factors play a role in influencing this regrowth:
- Severity of Hair Loss: Those with patchy alopecia often have a higher likelihood of regrowth compared to those with more extensive forms like alopecia totalis or universalis.
- Duration of Hair Loss: Early intervention can sometimes lead to better outcomes. If hair follicles remain dormant for an extended period, they may become less responsive to treatments aimed at stimulating regrowth.
- Age of Onset: Early onset of alopecia, particularly in childhood, can sometimes be associated with a prolonged course and reduced potential for complete regrowth.
- Presence of Other Autoimmune Conditions: As discussed earlier, individuals with other autoimmune conditions may experience a different trajectory with their alopecia, potentially influencing regrowth patterns.
- Treatments Undertaken: Some treatments, when administered appropriately, can enhance the potential for hair regrowth. This makes seeking consultation and intervention, potentially from centers like Haista Clinic, vital.
4.2 Potential for Recurrence and Hair Color Changes
Even with hair regrowth, there are certain considerations to bear in mind:
- Recurrence: While hair might regrow, there’s always a risk of recurrence of hair loss. Monitoring for new patches and being proactive in seeking treatment can help manage this aspect.
- Hair Color and Texture Changes: Initially, the regrown hair might appear white or lighter in color. Over time, it may regain its original color, although this isn’t guaranteed. Additionally, the texture of the new hair might differ, being finer or curlier than before.
In conclusion, while alopecia presents challenges, understanding the dynamics of hair regrowth and being equipped with the right information can help navigate the journey more effectively. Combining hope with informed choices, especially in partnership with experienced specialists, can pave the way for better outcomes and improved quality of life.
5. Navigating Treatment Paths for Alopecia Areata
Addressing alopecia requires a multifaceted approach. Depending on the severity, type, and individual needs, various treatments can be explored. It’s crucial to understand each option’s merits and considerations to make informed decisions tailored to the individual’s unique circumstances.
5.1 The Role of Medications in Managing Alopecia Areata
Medications form the cornerstone of many treatment strategies for alopecia:
- Corticosteroids: These are potent anti-inflammatory drugs that can suppress the autoimmune response causing hair loss. They can be taken orally or applied as a cream, although prolonged usage requires monitoring due to potential side effects.
- Minoxidil: Originally used for hypertension, topical minoxidil can stimulate hair growth and is often prescribed for alopecia, especially in its early stages.
- JAK Inhibitors: These are a newer class of drugs showing promise in treating alopecia by targeting specific pathways in the immune response.
5.2 Benefits of Intralesional Steroid Injections
For localized alopecia, intralesional steroid injections directly into the bald patches can be beneficial. They deliver a concentrated dose of steroids to the affected area, minimizing systemic side effects. Patients often witness hair regrowth within weeks of the treatment. However, the procedure might be slightly painful, and multiple sessions might be required for optimal results.
5.3 Topical Immunotherapy: A Closer Look
This treatment modality involves inducing an allergic reaction using chemicals like diphencyprone (DPCP) or squaric acid dibutylester (SADBE). The rationale is to divert the immune system’s attention from attacking the hair follicles to addressing the deliberately induced allergic reaction. Success rates vary, but it’s an option worth considering for extensive alopecia or when other treatments haven’t yielded desired outcomes.
5.4 Light Therapy Solutions
Also known as photochemotherapy, this approach involves the use of ultraviolet light in conjunction with a light-sensitizing medication. The treatment can stimulate hair growth by altering the immune response. However, multiple sessions are usually required, and there’s a need for careful monitoring due to potential side effects, including an increased risk of skin cancers.
5.5 Embracing Supportive Cosmetic Measures
While the focus is often on medical treatments, it’s essential to recognize the value of supportive cosmetic measures:
- Wigs and Hairpieces: Quality wigs can offer a natural appearance, providing not just aesthetic benefits but also boosting self-confidence.
- Hair Tattooing: This involves tattooing the scalp to give an illusion of short hair or stubble, often beneficial for those who prefer a shaved appearance.
- Scalp Micropigmentation: A more advanced version of hair tattooing, it offers a 3D appearance of natural hair follicles.
- Hair Growth Shampoos and Products: While they might not reverse alopecia, they can support overall scalp health, potentially aiding in the effectiveness of other treatments. Reputable clinics, such as Haista Clinic, often provide guidance on suitable products.
In summary, while alopecia can be challenging, numerous treatment avenues can be explored. Collaborative decision-making, in tandem with experienced professionals, ensures that each individual finds a path best suited to their needs, promoting both hair regrowth and emotional well-being.
6. Considering Hair Transplants for Alopecia Areata Patients
The journey of managing alopecia areata is multifaceted, and while various treatments focus on stimulating hair regrowth from existing follicles, hair transplantation emerges as a possibility for some. This procedure involves transplanting hair follicles from one part of the body to the balding areas. But is it a viable option for everyone with alopecia areata? Let’s delve deeper.
6.1 The Potential and Limitations of Hair Transplants
Hair transplantation can indeed offer a more permanent solution for those struggling with hair loss. The transplanted hair, once settled, grows naturally and can be cut, styled, or even dyed. But there are considerations:
- Success Rate: The success of a hair transplant largely depends on the quality of the donor’s hair. For those with alopecia areata, the unpredictable nature of the condition can impact the success rate.
- Potential for Scarring: Any surgical procedure carries risks, and scarring can be a concern, though modern techniques have significantly reduced this risk.
- Cost: Hair transplants can be expensive, and it’s crucial to weigh the benefits against the financial investment. For a detailed insight into the expenses, one can refer to resources like this guide on the cost of hair transplants in Turkey.
6.2 Importance of Evaluating the Disease State
Before considering a hair transplant, it’s vital to evaluate the state of alopecia areata:
- Stability: It’s recommended that the disease be stable for at least a year before the procedure. A flare-up post-transplant can compromise the results.
- Extent of Hair Loss: Those with widespread hair loss, like alopecia universalis, might not have sufficient donor hair for the procedure.
- Age: The pattern of hair loss can change over time. Younger patients might see their hair loss pattern evolve, making it challenging to predict the best approach for transplantation.
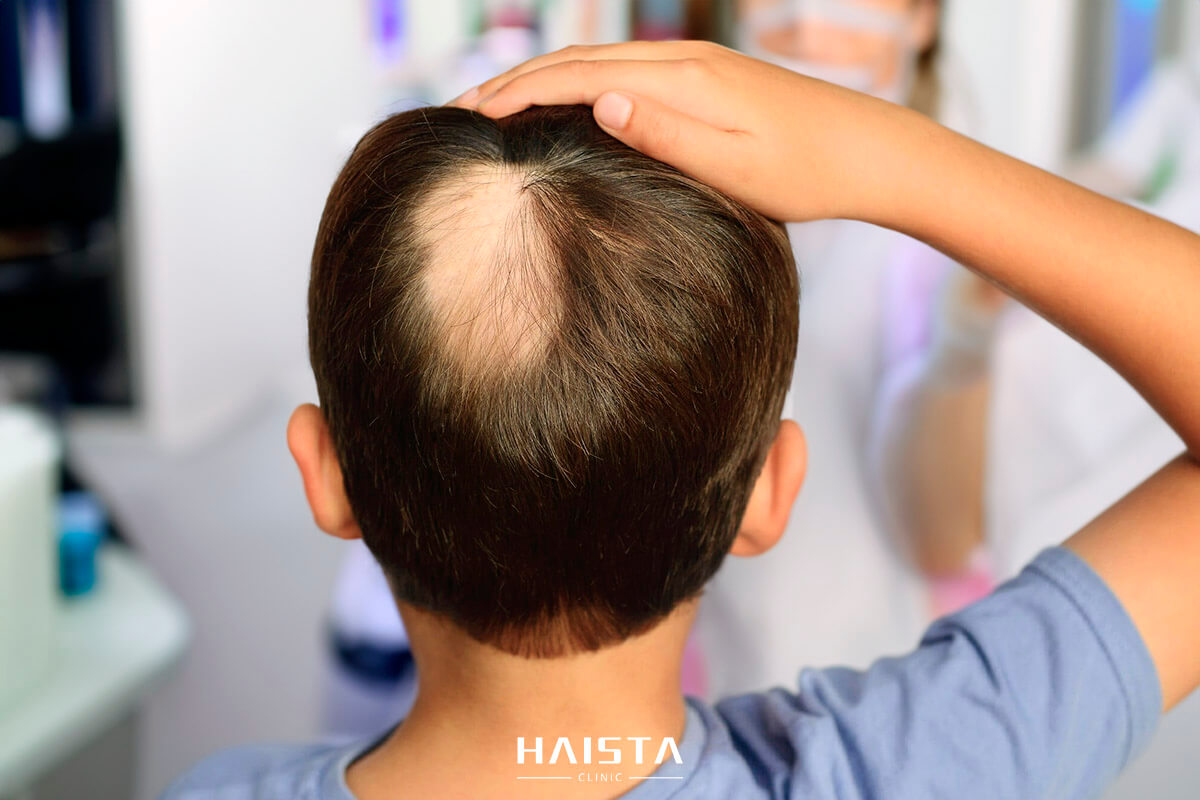

6.3 Ensuring Safe and Effective Transplantation
For those who are candidates for hair transplantation, ensuring the procedure’s safety and efficacy is paramount:
- Choosing the Right Clinic: The expertise of the surgeon and the clinic’s facilities play a critical role in the outcomes. Centers like Haista Clinic emphasize the importance of individualized care and state-of-the-art techniques.
- Post-Procedure Care: Aftercare is as crucial as the procedure itself. Adhering to guidelines, such as those in this comprehensive guide on hair transplant aftercare, can significantly impact the transplant’s success.
- Setting Realistic Expectations: While hair transplantation can be transformative, it’s essential to have a clear understanding of what to expect in terms of density, coverage, and growth patterns.
In conclusion, while hair transplantation offers hope to many with hair loss, its consideration for alopecia areata patients requires careful thought, expert consultation, and a clear understanding of the potential outcomes. As with any medical decision, being well-informed and partnering with experienced professionals ensures the best possible results.
7. Expert Opinions and Consultation
In the realm of medical treatments, especially concerning conditions like alopecia areata, a one-size-fits-all approach seldom yields optimal results. The uniqueness of each individual’s journey with the disease necessitates a tailored strategy, underpinned by expert opinions and thorough consultations.
7.1 Why Individualized Treatment is Essential
Alopecia areata is not just about patchy hair loss; it’s a story of genes, environment, emotions, and a multitude of factors interplaying in unique patterns for each individual. Here’s why personalization in treatment is non-negotiable:
- Diverse Genetic Makeup: Even if alopecia areata runs in a family, the onset, progression, and response to treatments can vary widely among family members due to their unique genetic makeup.
- Different Triggers: What exacerbates the condition in one person might be entirely different from another. Recognizing and addressing these triggers can only be achieved through a bespoke treatment plan.
- Variable Psychological Impact: The emotional toll of alopecia areata is profound. An individualized approach ensures that emotional and psychological needs are addressed alongside physical treatments.
7.2 Seeking Guidance: The Importance of Professional Consultation
Professional consultation acts as the compass in navigating the complexities of alopecia areata:
- Diagnosis Confirmation: Before embarking on any treatment journey, it’s vital to confirm the diagnosis. Several conditions mimic alopecia areata, and only an expert can differentiate with certainty.
- Tailored Treatment Plans: A professional can craft a treatment plan based on the patient’s unique needs, considering the disease’s state, individual preferences, and potential risks and benefits of various treatments.
- Continuous Monitoring: Alopecia areata’s unpredictable nature means regular check-ups are essential. Changes in the condition can be addressed promptly with the guidance of a professional.
- Emotional Support: Beyond physical treatments, professionals can provide or recommend counseling and support groups, helping individuals cope with the emotional aspects of hair loss.
For those contemplating surgical interventions like hair transplants, it becomes even more crucial to engage in thorough consultations with clinics known for their expertise, such as Haista Clinic, to understand the procedure’s intricacies and make informed decisions.
In essence, while the journey with alopecia areata might seem daunting, expert opinions and consultations illuminate the path, ensuring that every step taken is well-informed, safe, and aligned with the individual’s holistic well-being.
8. Conclusion and Next Steps
Alopecia areata, characterized by its unpredictable nature and profound emotional impact, has been a subject of extensive research and countless personal journeys. While it may present challenges, the growing understanding of its causes, manifestations, and treatment options illuminates a path forward for those affected.
Taking charge of one’s journey with alopecia areata requires a multifaceted approach:
- Stay Informed: Knowledge is power. Continuous self-education about the condition, its latest research findings, and emerging treatments will equip individuals to make empowered decisions.
- Prioritize Expert Consultations: Engaging regularly with healthcare professionals ensures that one’s approach to managing alopecia areata is evidence-based and tailored to individual needs.
- Consider All Options: From medications to surgical interventions like hair transplants, it’s essential to weigh the pros and cons of each treatment and decide on a path that aligns with one’s comfort and desired outcomes.
- Embrace Support: Connecting with support groups, therapists, or counselors can make a significant difference. Sharing experiences, challenges, and triumphs with others can be both therapeutic and enlightening.
- Continuous Monitoring: Given the condition’s unpredictability, regular check-ups and staying attuned to any changes in the pattern or extent of hair loss can ensure timely interventions.
For those leaning towards the possibility of hair transplants, resources such as Haista Clinic’s guide on hair transplants in Istanbul can provide comprehensive insights.
In essence, while alopecia areata may bring its set of challenges, it also offers an opportunity for resilience, self-discovery, and a deeper understanding of oneself. With the right resources, expert guidance, and a supportive community, navigating this journey can lead to empowering outcomes and renewed confidence.
FAQ
Q: What exactly is alopecia areata?
A: Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition where the immune system mistakenly targets hair follicles, leading to hair loss. It usually presents as coin-sized round patches of baldness.
Q: Is alopecia areata hereditary?
A: While not strictly hereditary, there is a genetic component to alopecia areata. If a family member has the condition, the chances of another member developing it are slightly higher.
Q: Can stress cause alopecia areata?
A: While the direct cause of alopecia areata is still under study, there’s evidence suggesting that emotional and psychological stress can act as a trigger in some individuals.
Q: Is hair loss from alopecia areata permanent?
A: Not always. Many individuals with alopecia areata experience hair regrowth within a year. However, the extent and rate of regrowth can vary, and recurrence is possible.
Q: Can I undergo a hair transplant if I have alopecia areata?
A: Hair transplants might be an option for some individuals with alopecia areata. It’s crucial to consult with experts, like those at Haista Clinic, to determine suitability and potential outcomes.
Q: Are there any treatments available for alopecia areata?
A: Yes, treatments range from medications and topical solutions to light therapy and even hair transplants. The choice of treatment depends on the extent of hair loss and individual preferences.
Q: How common is alopecia areata?
A: Alopecia areata affects approximately 1-2% of the population at some point in their lives. It can occur in individuals of all ages, genders, and ethnicities.
Q: How can I cope with the emotional impact of alopecia areata?
A: Seeking support from therapists, counselors, or joining alopecia areata support groups can be immensely helpful. Sharing experiences and coping strategies with others can provide comfort and understanding.
Q: Can alopecia areata lead to complete baldness?
A: In rare cases, alopecia areata can progress to alopecia totalis (complete scalp hair loss) or alopecia universalis (loss of all body hair).
Q: Are there any preventive measures for alopecia areata?
A: As the exact cause of alopecia areata is still being researched, there’s no surefire way to prevent it. However, managing stress and seeking early treatment upon noticing symptoms can help in managing the condition better.
By keeping oneself informed and seeking expert guidance, individuals can navigate the complexities of alopecia areata with confidence and hope.
Sources:
Alopecia Areata: Everything You Need to Know (American Academy of Dermatology Association)
Alopecia Areata (National Alopecia Areata Foundation)
Alopecia Areata: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment (Mayo Clinic)
Alopecia Areata: What Is It, What Causes It, and How Is It Treated? (Healthline)
Alopecia Areata: A Comprehensive Guide (DermNet NZ)





